Let a bar of semiconductor carry a current I and lie in a transverse magnetic field B. because of a phenomenon known as hall effect, an electric field E is induced. The direction of electric field E is perpendicular to both I and B. This effect is used to find the type of semiconductor (P-type or N-type), carrier concentration and also to measure conductivity δ and hence find mobility µ.
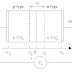
Fig.1: Shows a bar of semiconductor having width "d" and thickness "t". the current "I" is in the positive "x" direction and the magnetic field "B" is the positive "z" direction. A force will be exerted on the carriers are electrons and these electrons will be forced downwards. Therefore, terminal 1 will become negative with respect to terminal 2. A potential difference
EN (Known as Hall Voltage)
Fig.1: Shows a bar of semiconductor having width "d" and thickness "t". the current "I" is in the positive "x" direction and the magnetic field "B" is the positive "z" direction. A force will be exerted on the carriers are electrons and these electrons will be forced downwards. Therefore, terminal 1 will become negative with respect to terminal 2. A potential difference
EN (Known as Hall Voltage)





0 on: "Hall Effect"