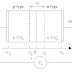
The most transistor circuits operate with the emitter terminal as common to the input and output circuits. This is known as CE connection and is shown Figure-1. In this connection the left hand loop is the base loop and the right hand loop is the connection loop. The base circuit controls the collector circuit.
Figure:(01) CE Connection of NPN Transistor
VBB is the base supply voltage and RB is the current limiting resistance in base circuit. VBE denote the voltage between the base and the emitter. VBB is
more than VBE. Typically VBB lies between 5 and 15 V in most circuits.
By changing VBB and RB. We can control the base current. The base current control the collector current. VCC is the collector supply voltage and VCE is the voltage between collector and emitter. RC is the current limiting resistance in the collector circuit. As before the base emitter junction is forward biased whereas the base collector junction is reverse biased. The currents IB, IE, IC are assumed positive when they flow into the transistor.
Figure-02 shows the output characteristics of the CE connection. These characteristics depict the relation between collector current IC and collector to emitter voltage (VCE) for different values of base current.
These characteristics are for a n-p-n transistor. These characteristics have three distinct region, i.e. active region, saturation region and breakdown region.
The active region is the region in which the curves are almost horizontal. VCE is between a fraction of 1V and a few volts. In this region, the collector junction is reverse biased and the emitter junction is forward biased. When a transistor is used as an amplifier, it must operate in this region only. The base current is IB = - (IC+IE)
By changing VBB and RB. We can control the base current. The base current control the collector current. VCC is the collector supply voltage and VCE is the voltage between collector and emitter. RC is the current limiting resistance in the collector circuit. As before the base emitter junction is forward biased whereas the base collector junction is reverse biased. The currents IB, IE, IC are assumed positive when they flow into the transistor.
Figure-02 shows the output characteristics of the CE connection. These characteristics depict the relation between collector current IC and collector to emitter voltage (VCE) for different values of base current.
These characteristics are for a n-p-n transistor. These characteristics have three distinct region, i.e. active region, saturation region and breakdown region.
The active region is the region in which the curves are almost horizontal. VCE is between a fraction of 1V and a few volts. In this region, the collector junction is reverse biased and the emitter junction is forward biased. When a transistor is used as an amplifier, it must operate in this region only. The base current is IB = - (IC+IE)







0 on: "Common Emitter (CE) Connection Of Transistor"