Resistor:
Resistance is one of the three passive elements of electric circuits. Every element has some amount of resistance. The resistance of leads capacitors and inductors can usually be ignored.
From circuit point of view a resistor is a device which shows a constant relation between the voltage drop across it and the current flowing through it. Thus it obeys ohm's law.
From the energy view point the resistance parameter can be thought of as a device capable of converting electrical energy into heat energy. The resistance parameter is a geometric constant as seen in equation below.
Here,
R= resistance (ohms,Ω)
l = Length (m)
A = Area of cross section (m2)

Resistors of values ringing from milli-ohm are used in a variety of circuits of electrical machines, instruments,electronics and heating devices. They are classified into wire wound and carbon composition resistors.
Resistance is one of the three passive elements of electric circuits. Every element has some amount of resistance. The resistance of leads capacitors and inductors can usually be ignored.
From circuit point of view a resistor is a device which shows a constant relation between the voltage drop across it and the current flowing through it. Thus it obeys ohm's law.
From the energy view point the resistance parameter can be thought of as a device capable of converting electrical energy into heat energy. The resistance parameter is a geometric constant as seen in equation below.
Here,
R= resistance (ohms,Ω)
l = Length (m)
A = Area of cross section (m2)
Resistors of values ringing from milli-ohm are used in a variety of circuits of electrical machines, instruments,electronics and heating devices. They are classified into wire wound and carbon composition resistors.
Conductor:
Capacitor:
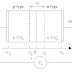
A capacitor is a device capable of strong electric charge. It is one of three passive elements of electric circuits. It consist of two insulated parallel metallic plates with air or any other insulating material in between.
Above Fig. shows two conductive parallel plates separated by an air space and connected to a battery/source. It consists of two insulated parallel metallic plates with air or any other insulating materials in between.






0 on: "Resistor, Conductor,Insulator, Capacitor & Inductor"